Building an ISO 45001 Compliant HSE Management System
An effective HSE (Health, Safety, and Environment) management system aligned with ISO 45001 provides a structured approach to managing safety risks and ensuring workplace safety. It not only minimizes workplace hazards but also ensures legal and regulatory compliance, helps improve operational efficiency, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Why Your Workplace Needs a Formal HSE System
A robust Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) management system is vital to ensure a safe and productive workplace. Aligned with global standards like ISO 45001, a formal HSE system enables businesses to take a structured approach to managing safety risks, legal compliance, and environmental protection.
This system not only reduces workplace hazards and incidents but also improves operational efficiency, reduces the risk of costly fines, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By implementing an HSE system, organizations demonstrate their commitment to protecting employees’ health and well-being, managing risks, and operating ethically—ultimately strengthening their reputation and boosting employee trust and customer confidence.
Core Steps to Design & Implement Your HSE System
1. Conduct a Safety Audit
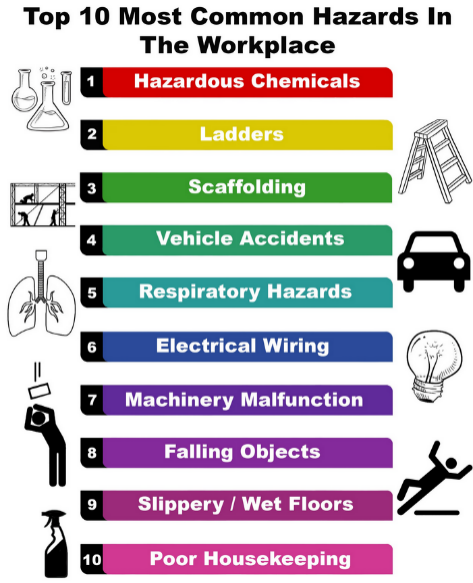
The first step in designing an effective HSE system is performing a comprehensive safety audit. This audit evaluates the existing risks, identifies unsafe practices, and highlights any compliance gaps in the current safety protocols. By uncovering hidden hazards or overlooked risks, the audit provides a clear foundation for the next steps in risk assessment and improvement.
Tools for Audit: Use a mix of site inspections, employee interviews, and data analysis. Consider using safety audit software for greater accuracy and efficiency.
2. Develop a Management Policy
Once risks have been assessed, create a clear HSE policy in line with ISO 45001 standards. This policy should outline the organization’s commitment to health, safety, and environmental management, clearly defining the roles, responsibilities, and authority of individuals involved in managing safety. It should also detail the procedures for communication, training, and risk management processes within the company.
Key Components: Roles and responsibilities, hazard identification, risk assessment process, emergency response, and continuous improvement.
3. Train and Educate Employees
Training is crucial in any successful HSE system. Consistent safety training on topics like workplace hazards, PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) use, safe operating procedures, and emergency protocols ensures employees are equipped to identify and mitigate risks.
Employee Engagement: Regular drills, scenario-based training, and clear communication can significantly boost employees’ safety awareness and engagement.
4. Track KPIs and Indicators
Measuring HSE performance is essential for continuous improvement. Track both leading indicators (e.g., safety observations, near-miss reports) and lagging indicators (e.g., Total Recordable Incident Rate – TRIR) to assess the effectiveness of your safety system. These indicators provide valuable data on the system’s performance and help identify areas for improvement.
Leading Indicators: Number of safety meetings, near-miss reports, safety inspections.
Lagging Indicators: Incident frequency, lost-time injuries, workers’ compensation claims.
5. Review and Improve Regularly
An HSE system is not a static framework—it must evolve. Regularly review your system’s performance through internal audits, management reviews, and employee feedback. Use this information to refine policies, address compliance gaps, and enhance the effectiveness of safety measures. Continuous improvement ensures the system remains dynamic and adaptable to emerging risks.
Tools for Review: Implement software to track safety audits, employee surveys, and incident data for easy reporting and analysis.


Key Benefits You Can Expect
1. Regulatory Compliance
A formal HSE system ensures your business stays compliant with local and international regulations. By adhering to industry standards like ISO 45001, you avoid costly fines and legal penalties associated with non-compliance.
2. Fewer Incidents
With a well-implemented HSE system, you can expect fewer incidents and accidents, reducing both injuries and illnesses. This not only protects employees but also prevents costly production delays, claims, and work stoppages.
3. Improved Morale
When employees feel safe and valued, their morale improves, leading to higher levels of productivity, job satisfaction, and engagement. A strong safety culture fosters trust and loyalty, resulting in lower turnover rates.
4. Better Reputation
Clients, stakeholders, and partners recognize organizations that prioritize safety and sustainability. By demonstrating a commitment to HSE, you enhance your company’s reputation, which can lead to more business opportunities, improved customer relationships, and greater market competitiveness.