Legal Responsibilities in Manual Handling Safety – What Employers Must Know
Manual handling is one of the biggest causes of workplace injuries worldwide, leading to back problems, sprains, and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). Because of its impact on worker health and business costs, governments and regulatory bodies have made manual handling safety a legal requirement.
Legal Responsibilities in Manual Handling: Why Compliance Matters
Manual handling is one of the leading causes of workplace injuries worldwide, often resulting in back problems, sprains, and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). These injuries not only affect workers’ health but also contribute to significant business costs. In recognition of this, governments and regulatory bodies have made manual handling safety a legal requirement.
Employers who fail to protect workers from manual handling risks are not only risking employee health but also face legal consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and reputation damage. In this blog, we’ll explore the legal responsibilities surrounding manual handling safety, why compliance is crucial, and how employers can effectively meet their obligations.



Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, p
Why Legal Compliance Matters in Manual Handling
Ignoring manual handling laws can have serious consequences, both for the health of employees and for the financial well-being of the business:
Employee Health Risks
Unsafe manual handling practices are directly linked to workplace injuries, including back injuries, strains, and long-term disability. Employees may suffer from chronic pain, requiring medical treatment, rehabilitation, and sometimes permanent changes to their ability to work.
Financial Costs
Employers face substantial financial costs when manual handling regulations are ignored. These include workers’ compensation claims, lost productivity, and fines. Additionally, injured workers may take extended sick leave, leading to further financial burdens for the company.
Reputation Damage
Failing to comply with manual handling regulations can severely harm an organization’s credibility. Companies that neglect worker safety risk their public image, which can affect customer trust, investor relations, and employee morale.
Legal Liability
Employers who do not adhere to manual handling laws may face legal action. This could include investigations, fines, and in extreme cases, criminal charges. Non-compliance can also lead to prolonged legal battles that disrupt business operations and damage a company’s reputation.
Employer Responsibilities Under Law
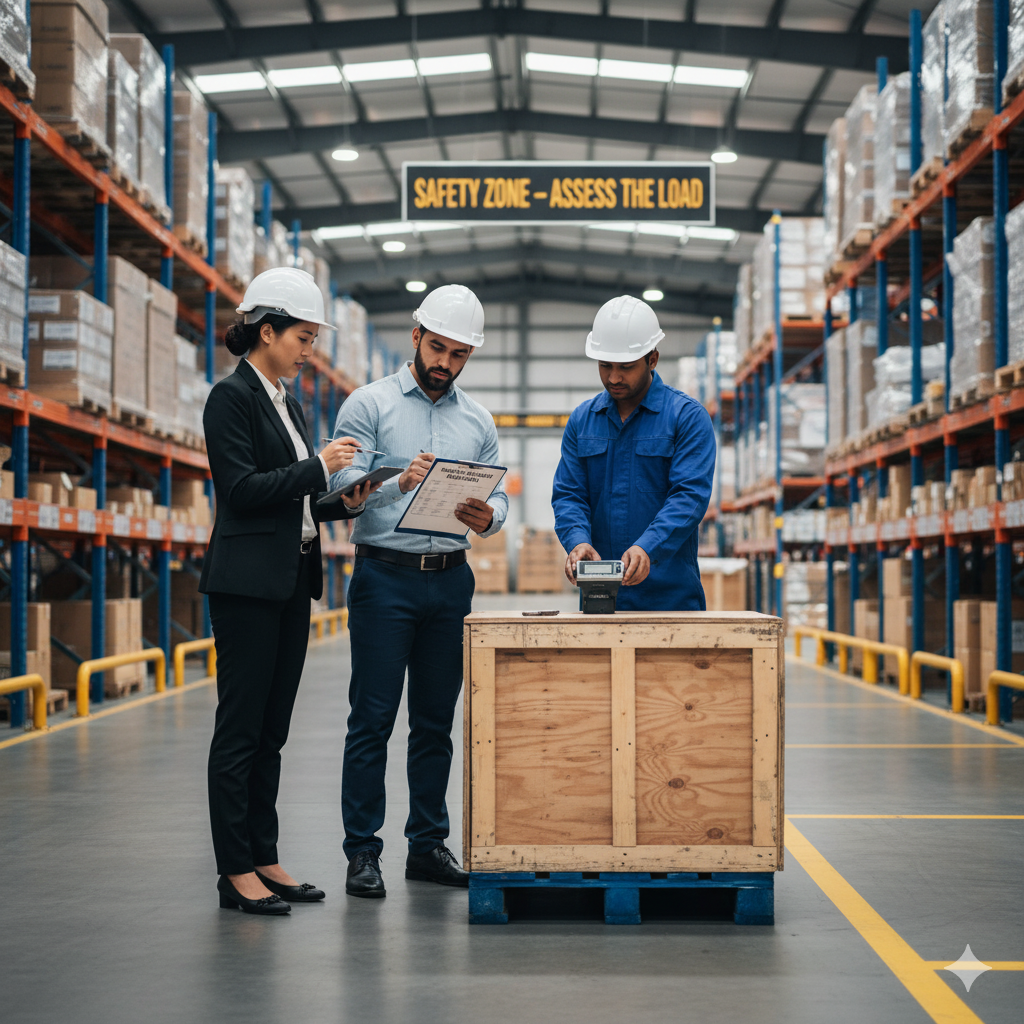
1. Risk Assessment
Employers are legally required to assess manual handling tasks for risks. This involves identifying:
Heavy loads
Awkward postures
Repetitive movements
Unsafe work environments
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly and should involve workers to identify potential hazards that may not be immediately obvious.
Tip: Use a manual handling risk assessment checklist to help identify these risks and implement corrective measures.
2. Avoid Hazardous Manual Handling Where Possible
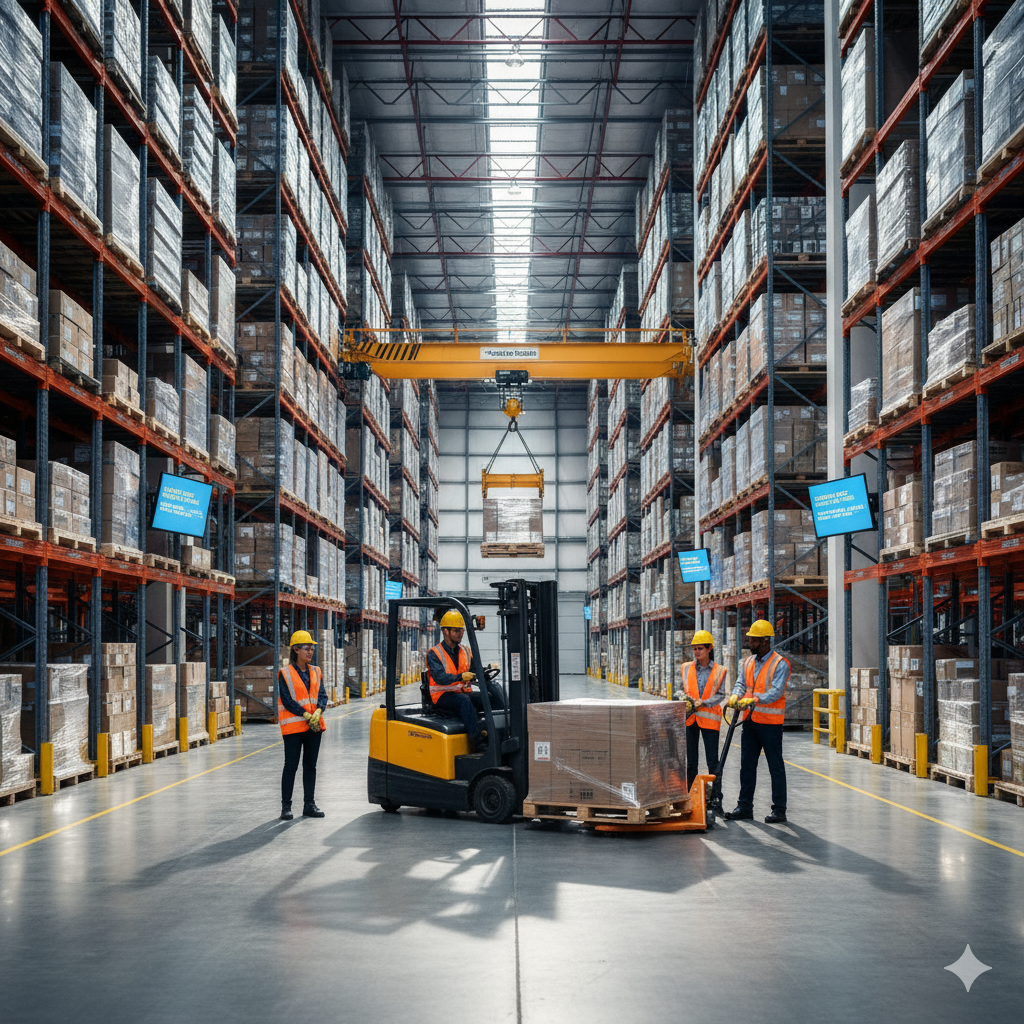
Regulations mandate that employers must eliminate manual handling risks whenever reasonably practicable. This could mean replacing manual lifting with mechanical aids such as forklifts, hoists, or conveyors to reduce the physical strain on workers.
Example: Instead of having workers manually move heavy loads, provide trolleys or automated conveyor systems to reduce manual handling.
3. Reduce Risks if Elimination Isn’t Possible
If manual handling cannot be fully eliminated, employers must reduce the associated risks through:
Proper equipment (e.g., adjustable workstations, lifting aids)
Safe work systems (e.g., two-person lifting, job rotation)
Task rotation to avoid repetitive strain injuries
Tip: Implement regular ergonomics training to ensure workers are using the correct posture and lifting techniques.
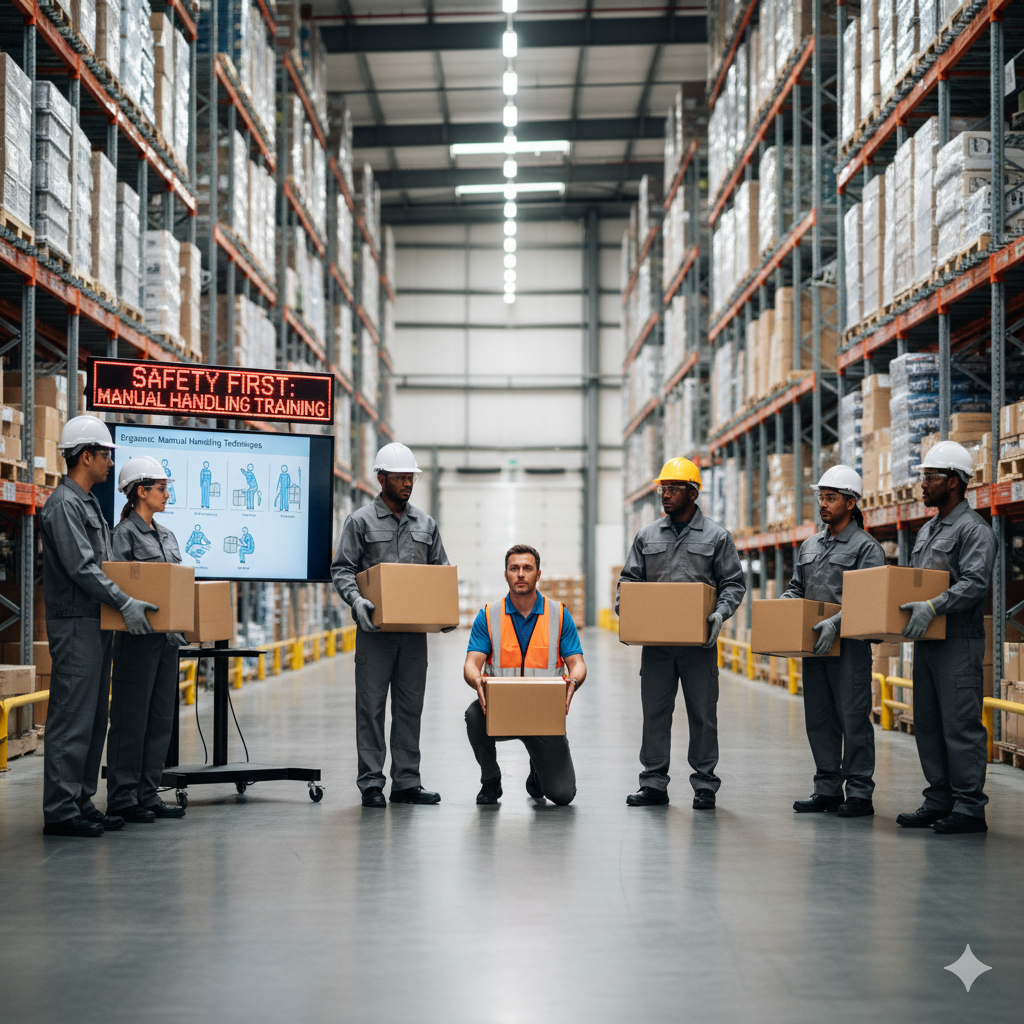
4. Provide Training and Information
Employees must receive proper training in:
Safe lifting techniques
Correct use of equipment (e.g., forklifts, hoists)
Hazard awareness and how to identify risks
Employers should also provide clear signage and guidance to reinforce safety practices.
5. Monitor and Review
Employers must regularly review manual handling practices and conduct safety audits to ensure compliance with laws. This helps to identify new risks or areas for improvement and keeps the workplace adaptable to changing conditions.
Tip: Conduct annual safety audits to identify new risks and ensure continuous improvement.
Employee Responsibilities Under Law
Legal compliance isn’t just the employer’s responsibility—employees also have duties under manual handling laws, such as:
Following training and safety instructions
Using provided equipment correctly
Reporting hazards or unsafe practices
This shared responsibility ensures that safety becomes a team effort, making it easier to maintain a safe work environment.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to follow manual handling regulations can lead to severe consequences, including:
Fines and Penalties
Safety authorities can impose heavy fines on businesses that fail to comply with manual handling regulations. These fines can add up quickly and significantly impact the business’s financial health.
Compensation Claims
Injured workers may file claims for medical expenses and lost income, further increasing financial costs for the business.
Legal Action
In the worst-case scenario, non-compliance can result in lawsuits or even criminal charges. This can cause lasting damage to a business’s reputation and financial stability.
Business Disruption
Investigations, downtime, and reputational damage from non-compliance can hurt operations and customer relationships.
Best Practices for Compliance
✅ Carry Out Regular Manual Handling Risk Assessments
By regularly assessing tasks and work environments, businesses can identify and mitigate risks before they lead to injuries.
✅ Invest in Ergonomic Equipment and Mechanical Aids
Providing lifting aids, such as forklifts, trolleys, and hoists, is cheaper than paying for injuries.
✅ Provide Ongoing Training and Refresher Sessions
Regular training ensures that workers understand the importance of safe manual handling and follow proper techniques.
✅ Encourage a Safety-First Workplace Culture
Creating a culture of safety encourages workers to report unsafe practices and follow procedures that prevent injuries.
✅ Keep Detailed Records of Training, Incidents, and Safety Measures
Documenting safety practices, training sessions, and incident reports helps demonstrate compliance and identify areas for improvement.
ulvinar dapibus leo.