Real-Life Case Studies of Manual Handling Injuries and Lessons Learned
Manual handling injuries are among the most common workplace incidents worldwide. From back strains to long-term musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), poor lifting techniques and unsafe practices can have life-changing consequences for workers. While safety guidelines and training exist, accidents still happen when manual handling risks are underestimated.
The Future of Manual Handling Safety: How Technology Is Reshaping the Workplace
Workplace safety has always been a top priority, but as industries evolve, so do the risks faced by workers. One of the most persistent hazards is manual handling—lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling loads. Despite the best safety practices, manual handling injuries remain one of the most common causes of workplace accidents. Traditionally, safety relied on training and ergonomic practices, but now, technology is reshaping manual handling safety like never before.
Incorporating technology into manual handling not only enhances safety but also boosts productivity and reduces costs. With the integration of smart devices, mechanical aids, and even artificial intelligence (AI), manual handling risks are minimized, allowing businesses to foster safer working environments.



Why Manual Handling Needs Technological Support
Even with the best training programs, human error, fatigue, and physical limitations can still lead to injuries. That’s where technology steps in. By introducing safety devices, mechanical aids, and AI-powered systems, employers can effectively reduce manual handling risks, improve worker efficiency, and cut costs associated with workplace injuries.
Technological Innovations in Manual Handling
1. Mechanical Lifting Aids
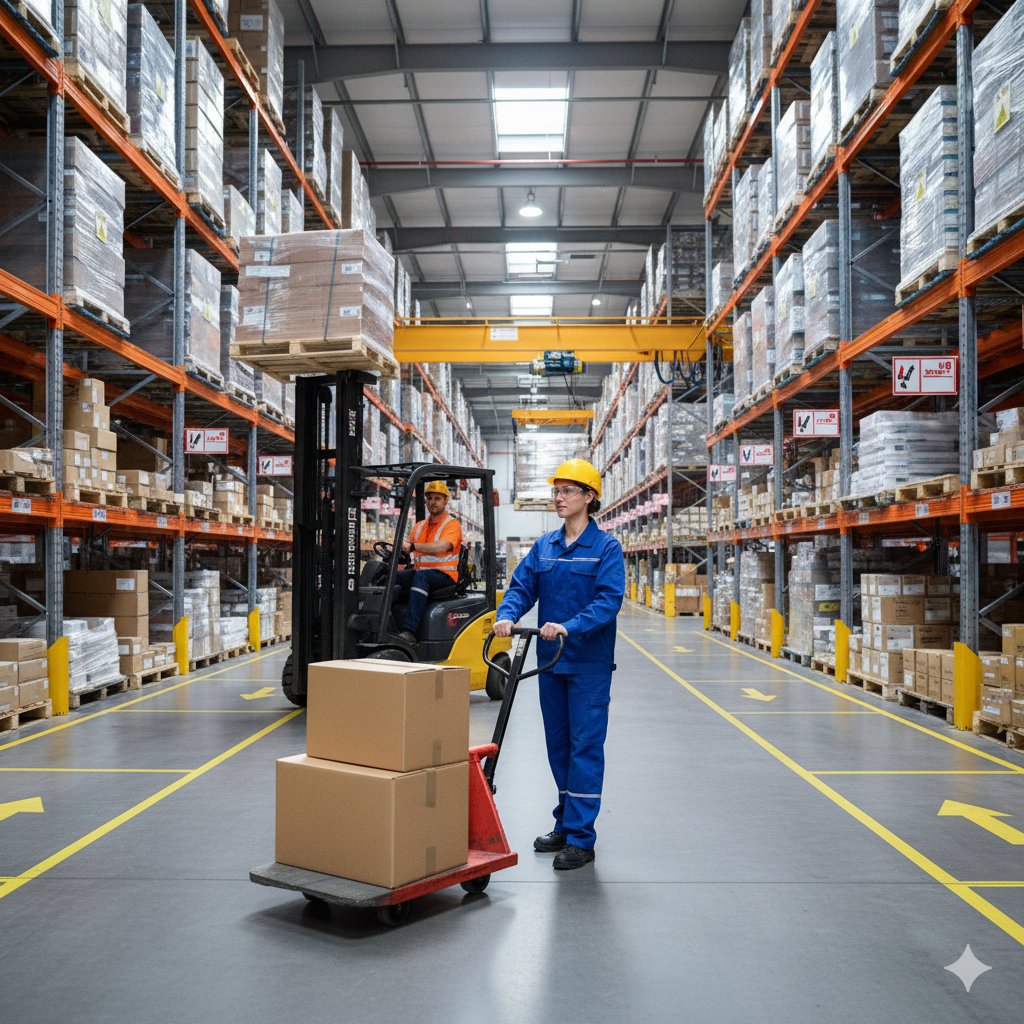
Devices such as trolleys, pallet trucks, forklifts, and hoists are now essential in most workplaces. These mechanical aids reduce the need for workers to lift heavy loads manually, minimizing the risk of back injuries, strains, and musculoskeletal disorders. Additionally, they speed up material handling tasks, leading to improved productivity.
Example: A warehouse using automated pallet jacks to move goods efficiently, reducing the risk of injuries from manual lifting.
2. Wearable Technology
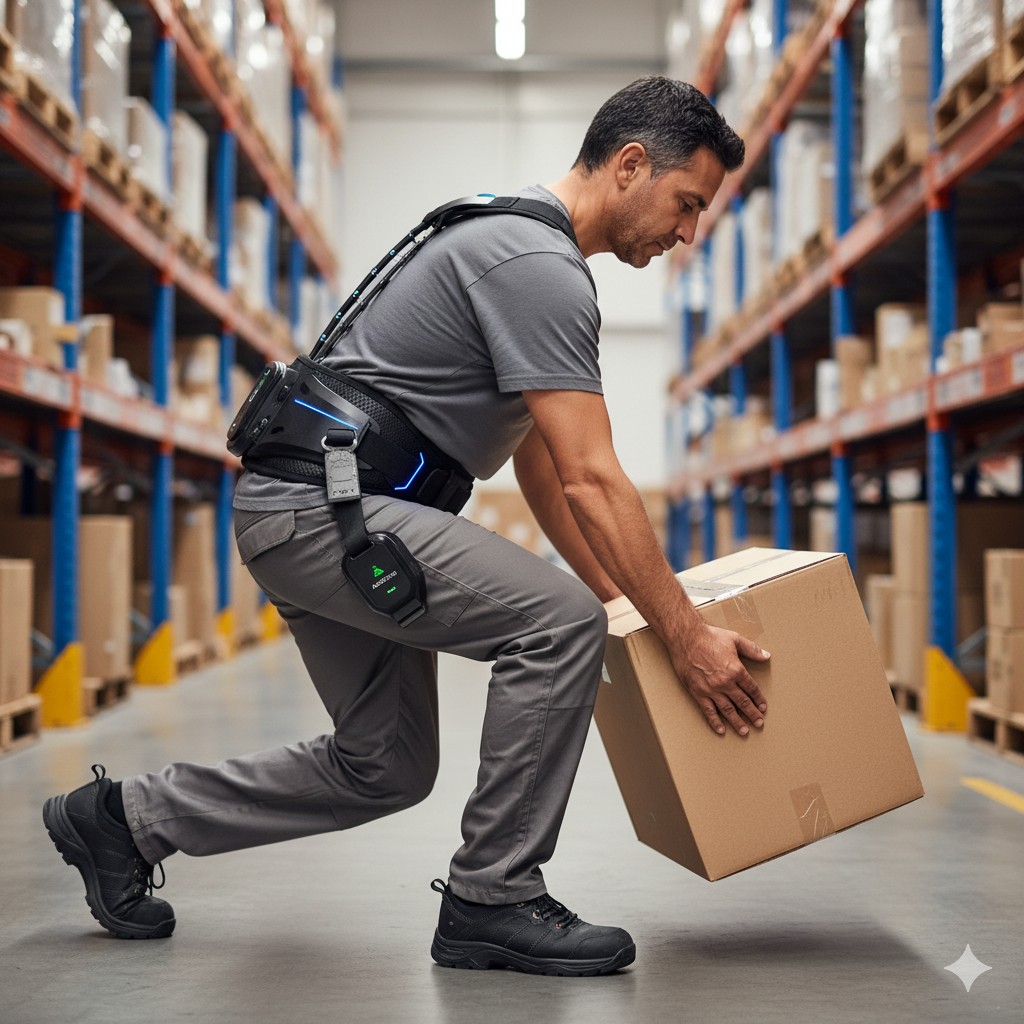
Smart belts, exoskeletons, and posture sensors are transforming manual handling safety. These wearable devices support workers’ backs, monitor movements, and provide real-time feedback. For instance, a smart belt can alert workers when they are bending incorrectly or lifting unsafely, helping to prevent musculoskeletal injuries before they occur.
Example: An exoskeleton worn by construction workers to reduce the strain on their back and joints while lifting heavy materials.
3. Automation & Robotics
Automated systems, like conveyor belts and robotic arms, are replacing repetitive manual lifting tasks, especially in high-volume environments such as warehouses and factories. These technologies reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) and improve overall efficiency. Robotics also ensure more precise handling, reducing human error.
Example: Robotic arms in a manufacturing plant lifting heavy parts and assembling products, reducing manual lifting entirely.
4. AI-Powered Risk Assessment Tools
Some businesses are now using AI and data analytics to assess manual handling risks and improve workplace safety. These tools analyze factors such as the weight of loads, the frequency of lifting tasks, and employee movements to identify dangerous patterns. AI can recommend adjustments to workflows and suggest improvements to reduce risks.
Example: AI-powered sensors track the frequency and intensity of manual lifting tasks and provide insights into potential ergonomic risks.
Benefits of Technology in Manual Handling Safety
✅ Reduced Injuries
With the integration of smart devices and lifting aids, workers experience fewer musculoskeletal injuries, improving overall health and safety.
✅ Improved Productivity
Tasks that once required multiple workers can now be done faster and more safely with the help of mechanical aids and robotic systems, leading to increased output.
✅ Real-Time Feedback
Wearable devices offer instant alerts on unsafe movements, allowing workers to correct their posture and avoid injuries before they happen.
✅ Employee Well-Being
Workers feel supported and protected when modern tools and technologies reduce the physical strain of manual handling.
✅ Cost Savings
Businesses save money by reducing compensation claims, medical costs, and downtime caused by manual handling injuries.
Challenges of Implementing Technology
While the benefits of incorporating technology into manual handling safety are significant, businesses must also consider the following challenges:
Initial Costs
High-tech equipment and devices like robotic arms, exoskeletons, and AI-powered sensors can be expensive upfront investments. However, the long-term savings from injury prevention and increased productivity often outweigh the initial costs.
Training Needs
Employees need to be properly trained to use new tools and technologies effectively. Providing this training can take time and resources but is necessary to maximize the potential of the technology.
Maintenance
Mechanical and digital systems require regular maintenance to ensure they function properly. Businesses need to budget for repair costs and ensure that technology is consistently operational.
The Future of Manual Handling Safety
As industries move toward Industry 4.0, the role of technology in manual handling safety will only expand. We can expect:
Advanced AI-driven safety monitoring systems that continuously assess and adjust risk levels.
Wider adoption of wearable exoskeletons for workers in industries like construction and manufacturing to reduce strain.
Increased automation in workplaces, completely removing high-risk manual handling tasks and improving operational efficiency.
The future is clear: technology will play a central role in both protecting workers and improving business efficiency.
Conclusion
Manual handling safety has evolved from basic training and ergonomic practices to sophisticated technological solutions. Lifting aids, wearables, robotics, and AI-powered tools are making workplaces safer, improving worker health, and boosting productivity.
Employers who invest in modern safety technologies not only ensure compliance with safety standards but also future-proof their workforce against injuries, creating a healthier, more efficient, and safer workplace.