Ergonomics and Manual Handling Designing a Safer Workplace
Manual handling isn’t just about technique it’s also about the workplace environment. Ergonomics plays a vital role in reducing injuries by designing tasks, equipment, and workstations that fit the worker, not the other way around. Poor ergonomics often leads to repetitive strain injuries, back problems, and fatigue.
Ergonomics and Manual Handling: Creating a Safer Workplace
Manual handling is a major cause of workplace injuries across all industries. While proper lifting techniques are critical, the workplace environment itself plays a significant role in preventing injuries. Ergonomics, the science of designing tasks, equipment, and workstations to fit the worker, not the other way around, is key to reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries, back problems, and worker fatigue.
Employers who focus on ergonomic design can improve employee safety, enhance productivity, and reduce costs associated with workplace injuries.
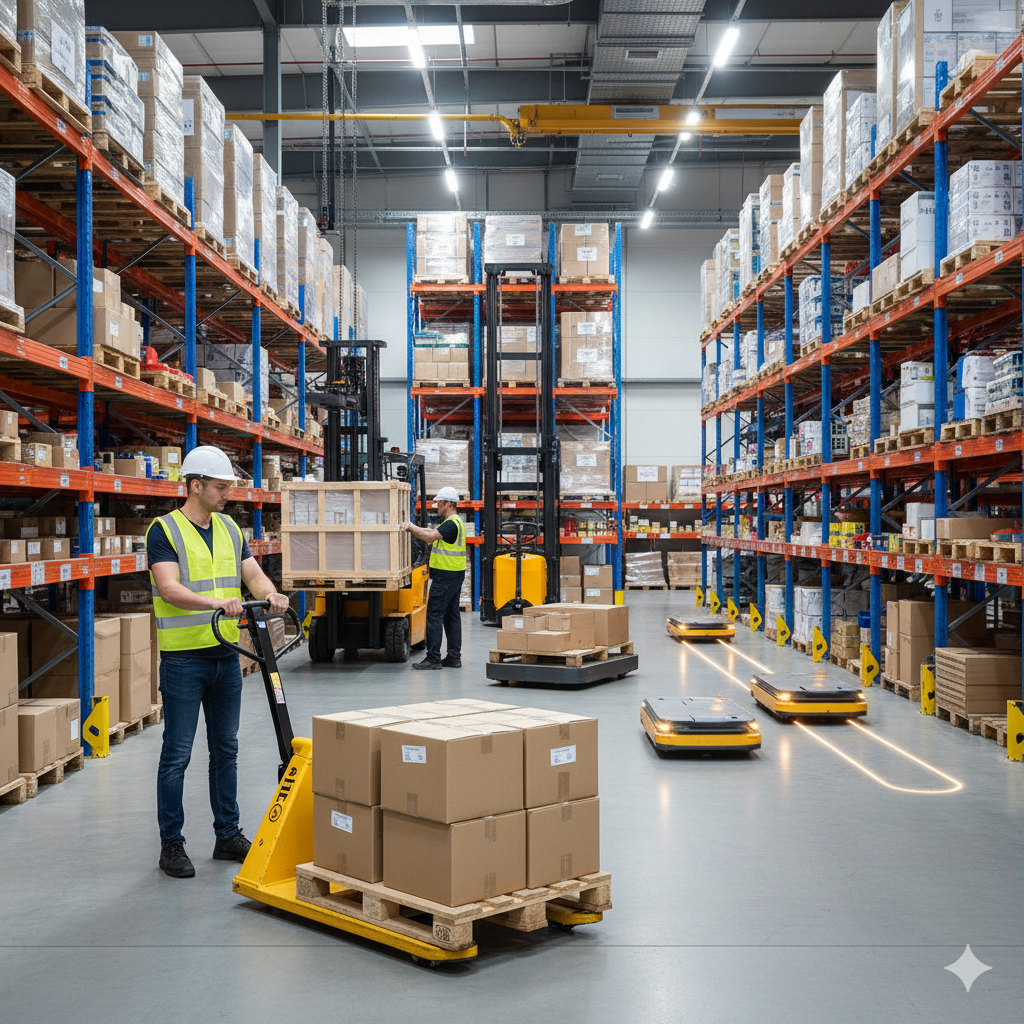
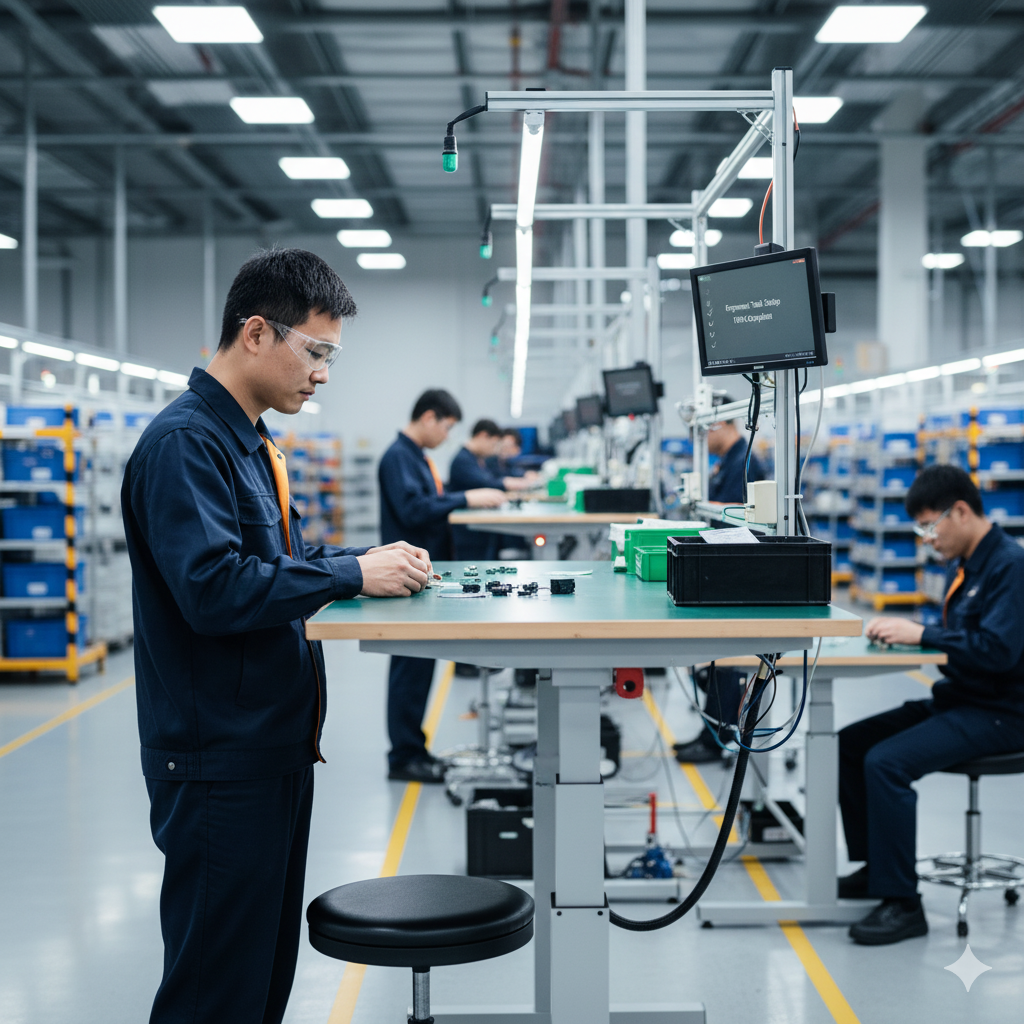
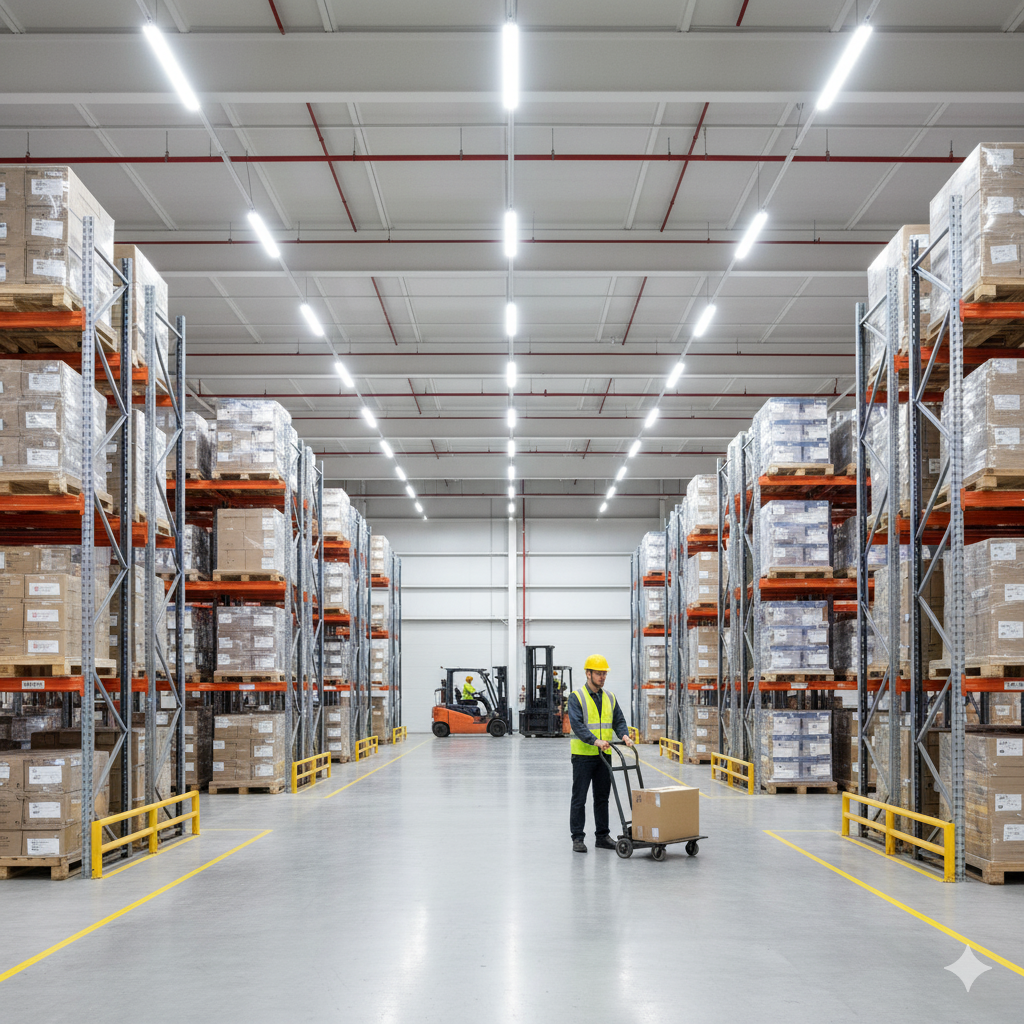



The Link Between Ergonomics and Manual Handling
Ergonomics involves designing work environments and tasks to suit human capabilities. When applied to manual handling, ergonomic principles can:
Reduce unnecessary lifting by ensuring materials are within easy reach.
Improve posture and reduce strain, preventing musculoskeletal injuries.
Prevent repetitive stress injuries by minimizing repetitive or awkward movements.
Create a safer, more comfortable workplace, boosting worker morale and efficiency.
Examples of Ergonomic Solutions
1. Adjustable Workstations
Workstations that can be raised or lowered allow employees to maintain neutral postures, reducing strain on the back, neck, and shoulders. This prevents excessive bending or reaching, which are common causes of manual handling injuries.
2. Mechanical Aids
Devices such as trolleys, conveyors, pallet trucks, and hoists can dramatically reduce the need for workers to lift heavy items manually, decreasing the risk of injury.
3. Proper Storage Design
Organizing storage so that heavy items are at waist height prevents employees from lifting objects from the floor or above shoulder level, reducing awkward postures.
4. Anti-Slip Flooring
Installing anti-slip mats or flooring prevents slips and falls, especially when workers are carrying heavy or awkward loads.
5. Adequate Lighting and Space
Ensuring that work areas are well-lit and have sufficient space allows employees to see hazards and move safely while performing tasks.
6. Ergonomic Tools
Using handles, grips, and tools designed for ergonomics reduces hand and wrist strain, particularly in repetitive tasks.
Benefits of Ergonomic Manual Handling
Implementing ergonomic principles in manual handling provides multiple benefits:
Fewer Injuries – Reducing awkward postures, repetitive strain, and heavy lifting directly lowers the risk of injury.
Higher Productivity – Comfortable workers are more efficient and can perform tasks with less fatigue.
Lower Costs – Reduces expenditures on injury claims, workers’ compensation, and sick leave.
Happier Workforce – Employees feel valued when their health and safety are prioritized, leading to higher morale and job satisfaction.
Integrating Ergonomics into Workplace Culture
To fully leverage ergonomic principles, employers should:
Conduct Workplace Ergonomic Assessments – Identify tasks that require frequent lifting, bending, or twisting.
Train Employees on Ergonomic Practices – Teach proper postures, lifting techniques, and the use of mechanical aids.
Provide Adjustable Equipment – Ensure workstations, chairs, and tools can be adapted to the worker’s height and body dimensions.
Encourage Feedback – Employees should report discomfort or hazards to improve ergonomic design.
Review Regularly – Continually assess and improve ergonomic solutions as tasks or equipment change.
By combining training, equipment, and environmental design, workplaces can dramatically reduce manual handling injuries while fostering a culture of safety.
Conclusion
Ergonomics is more than comfort—it is safety, efficiency, and well-being. By applying ergonomic principles to manual handling tasks, employers can:
Protect workers from injury.
Increase productivity.
Reduce costs associated with absenteeism and compensation claims.
Build a safe and supportive workplace culture.
A focus on ergonomics ensures that employees can perform manual handling tasks safely and effectively, creating a healthier, more efficient, and more motivated workforce.